Quick Start LeoFS with Java-client
July 28, 2014Introduction
This article will get you going with a how to develop and architect Java-client application for LeoFS. This article assumes that you have already installed LeoFS environment on your local or remote node. See Getting Started with LeoFS for more Information.
Installation and Setup S3 Java-client
The easiest way to install Java on your machine is through the yum or apt package installer. Then we need some additional Apache Ant.
CentOS, Fedora and RHEL:
##### Install Java, SDK and Dependencies #####
$ wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "https://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u5-b13/jdk-8u5-linux-x64.rpm"
$ sudo yum install jdk-8u5-linux-x64.rpm # To install JDK
$ sudo yum install ant # To install ant
Debian and Ubuntu based Installation
##### Install JAVA8, SDK and Dependencies #####
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installerdd-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java"
$ java -version # To Verfiy your installation
$ sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-set-default # To Setup java environment
###### Download Sample Project it includes aws-java sdk #####
$ git clone https://github.com/leo-project/leofs_client_tests.git
$ cd aws-sdk-java
About the sample
This sample application is designed to show you how to:
- Include a dependency on the aws-sdk using
build.xmlfile. - Read access keys from environment variables or define it statically in this sample we are using static entry.
- Instantiate an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) client using
ClientConfiguration()method. - Interact with Amazon S3 in various ways, such as creating a bucket and uploading a file.
The project's README file contains more information about this sample code. If you have trouble getting set up or have other feedback about this sample codes, let us know on GitHub.
API feature list
The storage API is compatible with the Amazon S3 REST API which means that any of the operations listed can be executed using any of the commonly available S3 libraries or tools.
Bucket-level operation
- GET Bucket - Returns a list of the objects within a bucket
- GET Bucket ACL - Returns the ACL associated with a bucket
- PUT Bucket - Creates a new bucket
- PUT Bucket ACL - Sets the ACL permissions for a bucket
- HEAD Object – Retrieves Bucket metadata.
- DELETE Bucket - Deletes a bucket
Object-level operation
- GET Object - Retrieves an object
- LIST Object - Retrieves an object list
- PUT Object - Stores an object to a bucket
- PUT Object (Copy) - Creates a copy of an object internally or externally
- HEAD Object - Retrieves object metadata (not the full content of the object)
- DELETE Object - Deletes an object
Multipart upload
- Initiate Multipart Upload - Initiates a multipart upload and returns an upload ID
- Upload Part - Uploads a part in a multipart upload
- Complete Multipart Upload - Completes a multipart upload and assembles previously uploaded parts
- Abort Multipart Upload - Aborts a multipart upload and eventually frees storage consumed by previously uploaded parts.
- List Parts - Lists the parts that have been uploaded for a specific multipart upload.
- List Multipart Uploads - Lists multipart uploads that have not yet been completed or aborted.
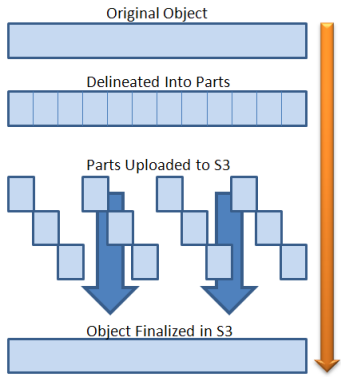
The multipart-upload allows you to upload a single object as a set of parts. Object parts can be uploaded independently and in any order. After all, parts are uploaded, LeoFS assembles an object out of the parts. When your object size reaches 100MB, you should consider using multipart uploads instead of uploading the object in a single operation. Read more about parallel multipart uploads.
Basically, AWS-Java Client have two types of the multipart upload method :
- Using the High-Level Java API for Multipart Upload
- Using the Low-Level Java API for Multipart Upload Here we are Using High-level Java API for the multipart upload. For more detail visit this page.
Sample methods:
The complete API reference is available on the Amazon site. Here we included our sample script file which includes major method which is supported by LeoFS.
Creating a connection
A simple way to specify your credentials is by injecting them directly into the factory method when instantiating the client object. However, be careful to NOT hard-coding your credentials inside your applications. Hard-coding your credentials can be dangerous. According to your bucket name, set sub-domain name entry as a per this page. For more detail method you can refer this page.
For More detail, you can refer this page.
Creating a bucket
A simple way to create bucket is given from here be careful bucket name should be globally unique and must be DNS compatible otherwise it will throw S3Exception. For more information about bucket name restrictions, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/BucketRestrictions.html bucket.
Does bucket exists ?
A simple to check bucket is exist or not and you have permission to access it. The operation returns a 200 - OK if the bucket exists and you have permission to access it. Otherwise, the operation might return responses such as 404 - Not Found and 403 - Forbidden. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
Get buckets
You can get list of all the buckets owned by your account using the listbuckets() method. You can also enumerate all buckets in your account. For more detail information you can refer this page.
Single-part object upload
A simple way to upload object via the single-part method from your file system which is recommended to use for object less than 100MB in size. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
Multi-part object upload
The multipart-upload allows you to upload a single object as a set of parts. Each part is a contiguous portion of the object's data. You can upload these object parts independently and in any order. If transmission of any part fails, you can retransmit that part without affecting other parts. After all, parts of your object are uploaded, LeoFS assembles these parts and creates the object. In general, when your object size reaches 100 MB, you should consider using multipart uploads instead of uploading the object in a single operation.
Advantages: Improved throughput, quick recovery from any network issues, suspend and resume object uploads begin an upload before you know the final object size. For more detail information, you can refer this page. This method is very simple in java for more detail you can refer this class methods.
Head an object
Files in Amazon-S3 and LeoFS are called objects and are stored in buckets. A specific object is referred to by its key (i.e., name) and holds data. Here we create a new object with the key name, HEAD request is metadata of that object.
e.g. ContentLength, ETag, ContentType etc.. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
READ an object
A simple way to download object from LeoFS in to current directory by using read method. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
Copy an object
A simple way to copy object on LeoFS same bucket or different bucket we should use this method than by using the exists method. we are checking presence of copied object. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
Move / Rename an object
This method currently not available via Java client but might be in future it will be available.
List a bucket’s content
Here we request an object iterator and loop over it to retrieve the desired information about the objects - object key, size, and modification time stamp in this case. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
Delete an object
A simple way to delete object from LeoFS by providing bucket and object name - key. The multiple object delete method currently not supported but you can perfrom similar operation via using iterator. For more detail information you can refer this page.
Currently, FileExist is not availble in built in AWS Java client. So I made my own trailer made method.
To dump InputStream into File I created a function dumpInputStream(InputStream,FileName). It will use to dump stream(string) into file.
To cound Hashtext(Etag) of local file to verify content's MD5 digest. I created a user define fucntion MD5(filePath) as below:
Get a bucket ACL
A simple way to get bucket ACL is given here. LeoFS basically supports private, public-read and public-read-write types of the ACL. Object level ACL is currently not supported yet. In java SDK it associated with CannedAccessControlList which have enume constant like Private,PublicRead, write and PublicReadWrite. For more detail information, you can refer this page. For more detail information about getBucketACL you can refer this page.
Put a bucket ACL
A simple way to put ACL and restrict different Bucket Acess by setBucketACl(BucketName,CannedAccessControlList) method. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
Delete a bucket
A simple way to delete bucket using deleteBucket(bucketName) method. For more detail information, you can refer this page.
Test script code:
This testing file include all well know methods of Java SDK. This script required sample file name as testFile at following location in $file_path = "../temp_data/$file_name"; your project Directory. Sample Operation testing Script which is located in downloaded project’s LeoFSSample.java file or you can access script.
Test script output :
You can check sample output of this script via this link.
comments powered by Disqus