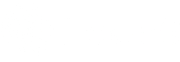LeoFS Storage¶
Fundamentals¶
LeoFS Storage consists of object and the metadata storage. In addition, it includes replicator and repairer in order to realise Eventual consistency.
In case of a write operation, LeoFS Storage accepts a request from LeoFS Gateway then automatically replicate an object into the LeoFS Storage cluster. Finally, LeoFS Storage confirms whether a stored object satisfy the consistency rule or NOT.
On the other hand, in case of a read operation, LeoFS Gateway requests a LeoFS Storage node. Then the LeoFS Storage node retrieves an object from the local object-storage or the remote LeoFS Storage node. Finaly, the LeoFS Storage node respond an object to the gateway. Also, the LeoFS Storage node checks consistency of the object with the asynchronous processing.
If the LeoFS Storage node finds inconsistency of an object, it will be recovered with the backend process. The object eventually keep consistensy with their functions.
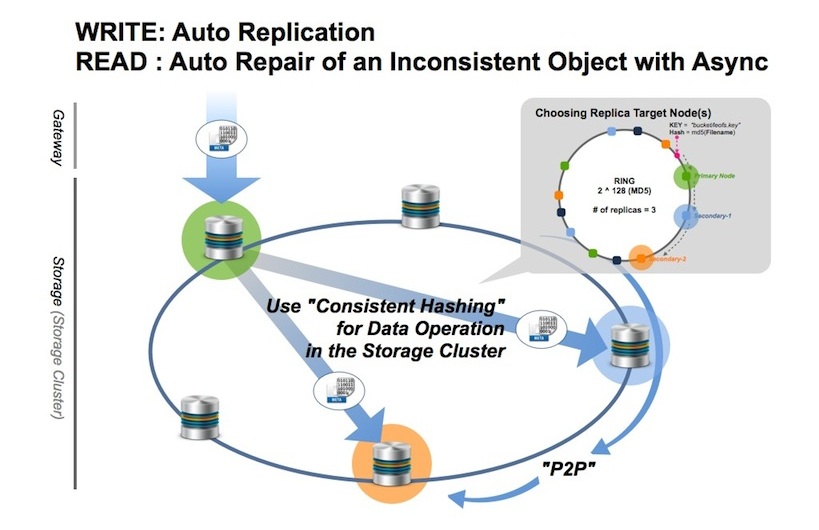
Data Structure¶
LeoFS’s object consists of 3 layers which are metadata, needle and object container.
- The object storage manages and stores both an object and a metadata, which merges as a needle.
- The metadata storage manages and stores attributes of an object which includes filename, size, checksum, and so on. And it depends of bitcask or leveldb.
- The object container is a log structured file format.
- This format is robust and high performance because effect of local file system is just a little part.
- LeoFS Storage is necessary to GC - the compaction mechanism in order to remove unnecessary objects from the object container.
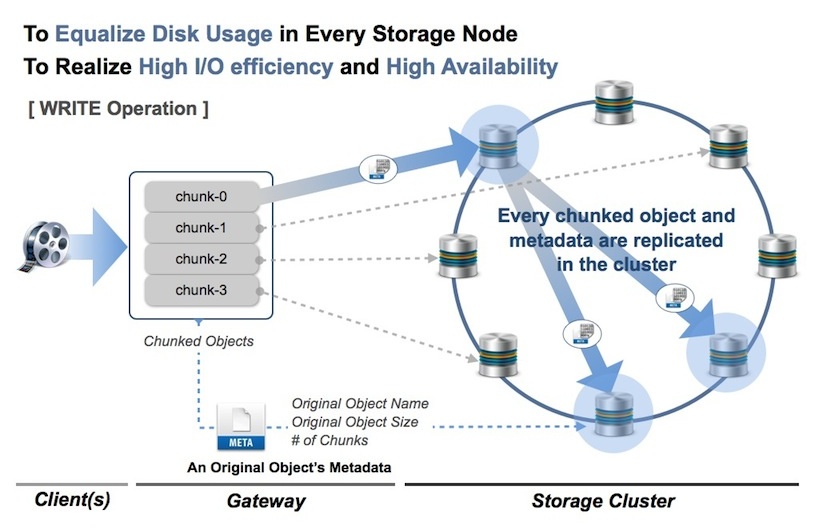
Large object support¶
- LeoFS supports to handle a large size object since v0.12. The purpose of this function is 2 things:
- 1st one is to equalize disk usage of every LeoFS Storage node.
- 2nd one is to realize high I/O efficiency and high availability.
In case of a write operation, a large size object is divided to plural objects at LeoFS Gateway then they’re replicated into the LeoFS Storage cluster similarly to a small size object. And also, the default chunk size is 5 mega bytes, value of which is able to change a custom chunked object size.
On the other hand, In case of READ of a large object, first, LeoFS Gateway retrieves a metadata of a requested object from a client. Then if it is a large size object, LeoFS Gateway retrieves the chunked objects in order of the chunk object number from the LeoFS Storage cluster. Finally, LeoFS Gateway responds the objects to the client.